 Key Value (KV) Store
Key Value (KV) Store
Available on: >= 0.18.0
Build stateful workflows with the KV Store.
Overview
Kestra's workflows are stateless by design. All workflow executions and task runs are isolated from each other by default to avoid any unintended side effects. When you pass data between tasks, you do so explicitly by passing outputs from one task to another and that data is stored transparently in Kestra's internal storage. This stateless execution model ensures that workflows are idempotent and can be executed anywhere in parallel at scale.
However, in certain scenarios, your workflow might need to share data beyond passing outputs from one task to another. For example, you might want to persist data across executions or even across different workflows. This is where the Key Value (KV) store comes into play.
KV Store allows you to store any data in a convenient key-value format. You can create them directly from the UI, via dedicated tasks, Terraform or through the API.
The KV store is a powerful tool that allows you to build stateful workflows and share data across executions and workflows.
How KV Store fits into Kestra's architecture
Kestra's architecture has been designed to offer a transparent separation between the orchestration and data processing capabilities. Kestra's Executor is responsible for executing tasks and workflows without directly interacting with the user's infrastructure. The Executor relies on Workers, which are stateless processes that carry out the computation of runnable tasks and polling triggers. For privacy reasons, workers are the only components that interact with the user's infrastructure, including the internal storage and external services.
Given that data persisted in the KV Store might contain sensitive information, the KV Store has been built on top of Kestra's internal storage. This ensures that all values are stored in the your private cloud storage bucket, and Kestra's database only contains metadata about the object, such as the key, file URI, any attached metadata about the object like TTL, creation date, last updated timestamp, etc.
In short, the KV Store gives you full control and privacy over your data, and Kestra only stores metadata about the KV pairs.
Keys and Values
Keys are arbitrary strings. Keys can contain:
- characters in uppercase and or lowercase
- standard ASCII characters
Values are stored as ION files in Kestra's internal storage. Values are strongly typed, and can be of one of the following types:
- string
- number
- boolean
- datetime
- date
- duration
- JSON.
For each KV pair, you can set a Time to Live (TTL) to avoid cluttering your storage with data that may only be relevant for a limited time.
Namespace binding
Key value pairs are defined at a namespace level and you can access them from the namespace page in the UI in the KV Store tab.
You can create and read KV pairs across namespaces as long as those namespaces are allowed.
UI: How to Create, Read, Update and Delete KV pairs from the UI
Kestra follows a philosophy of Everything as Code and from the UI. Therefore, you can create, read, update, and delete KV pairs both from the UI and Code.
Here is a list of the different ways to manage KV pairs:
- Kestra UI: select a Namespace and go to the KV Store tab — from here, you can create, edit, and delete KV pairs.
- Task in a flow: use the
io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Set,io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Get, andio.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Deletetasks to create, read, and delete KV pairs in a flow. - Kestra's API: use our HTTP REST API to create, read, and delete KV pairs.
- Kestra's Terraform provider: use the
kestra_kvresource to create, read, and delete KV pairs. - Pebble function: use the
kv()function to retrieve a value by key in a flow. - GitHub Actions: create, read, and delete KV pairs in your CI/CD pipeline.
The sections below provide detailed instructions on how to create and manage KV pairs using each of these methods.
Create new KV pairs from the UI
You can create, read, update, and delete KV pairs from the UI in the following way:
- Navigate to the
Namespacespage from the left navigation menu and select the namespace where you want to create the KV pair.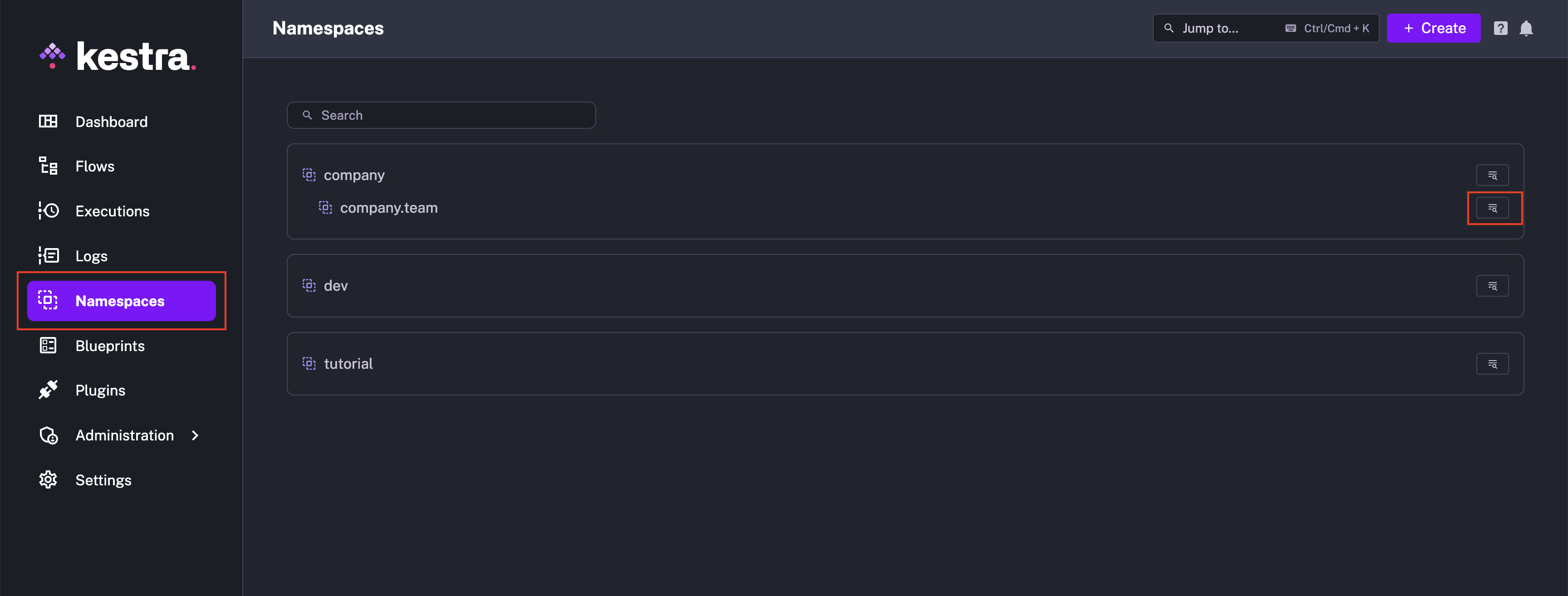
- Go to the
KV Storetab. This is where you can see all the KV pairs associated with this namespace.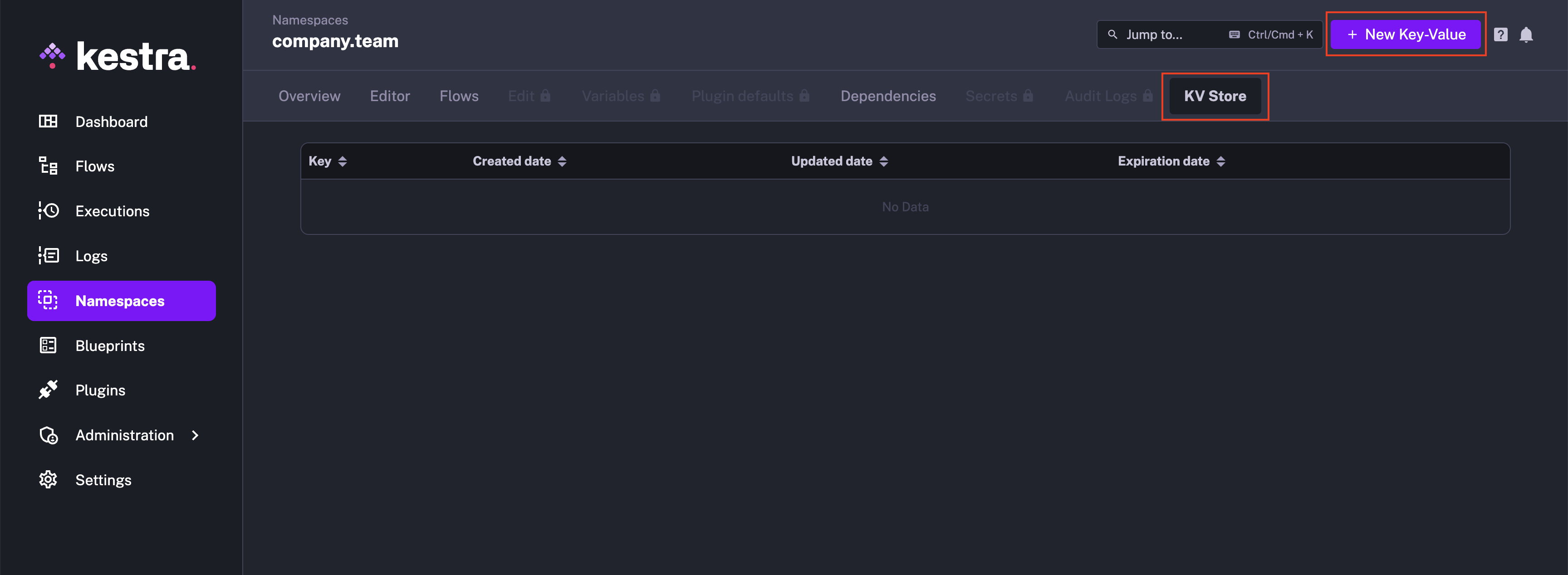
- Click on
New Key-Valuebutton in the top right corner to create a new KV pair. Enter a name for theKeyand assign a suitableTypefor the value — it can be a string, number, boolean, datetime, date, duration, or JSON.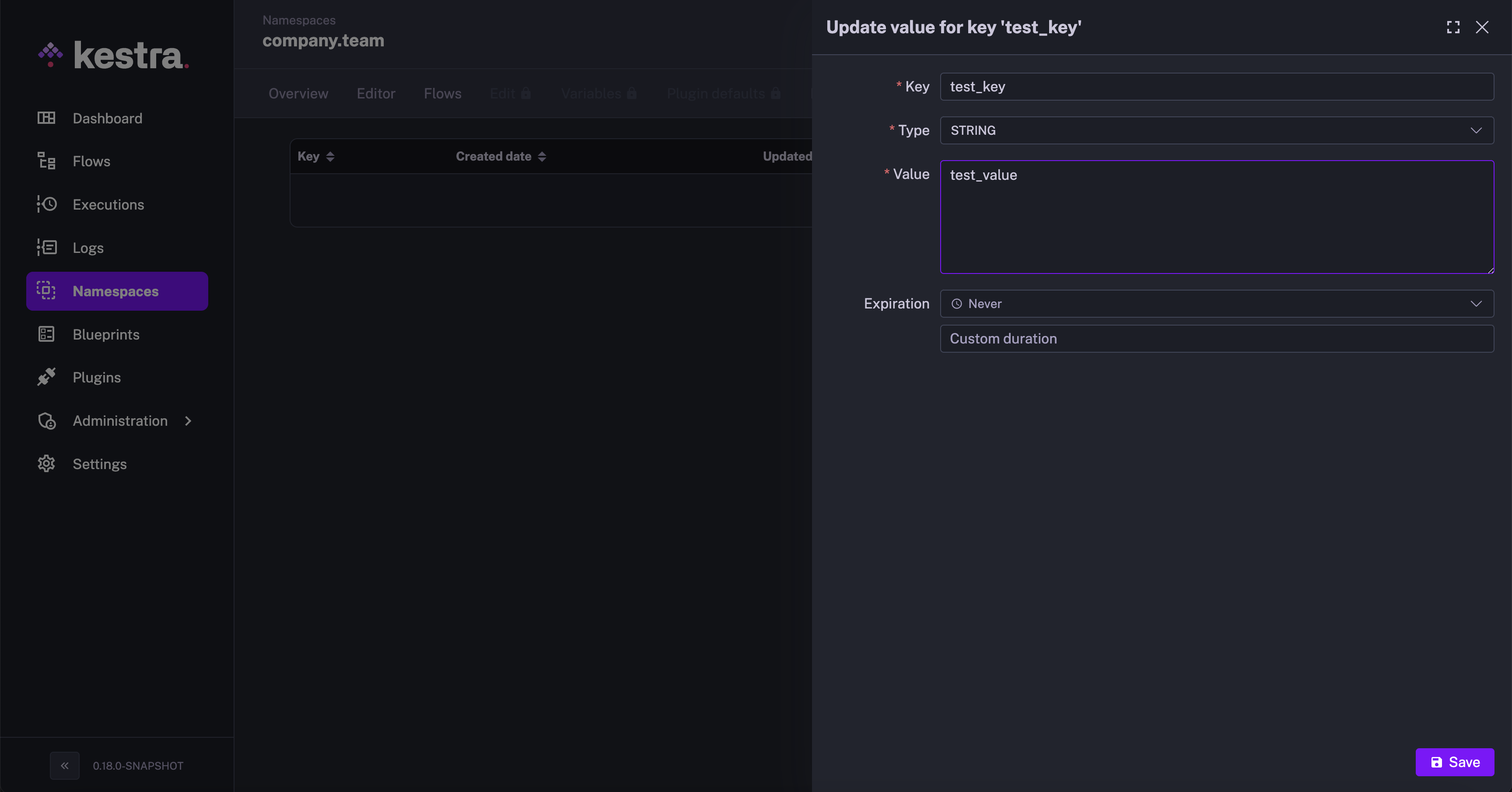
- Enter the value in the
Valuefield. - Optionally, you can configure a Time to Live (TTL) for the KV pair. The dropdown contains some standard durations. You can also select
Custom durationto enter a custom duration as a string in ISO 8601 duration format. - Finally,
Savethe changes. Your new KV pair should now be displayed in the list of KV pairs for that namespace.
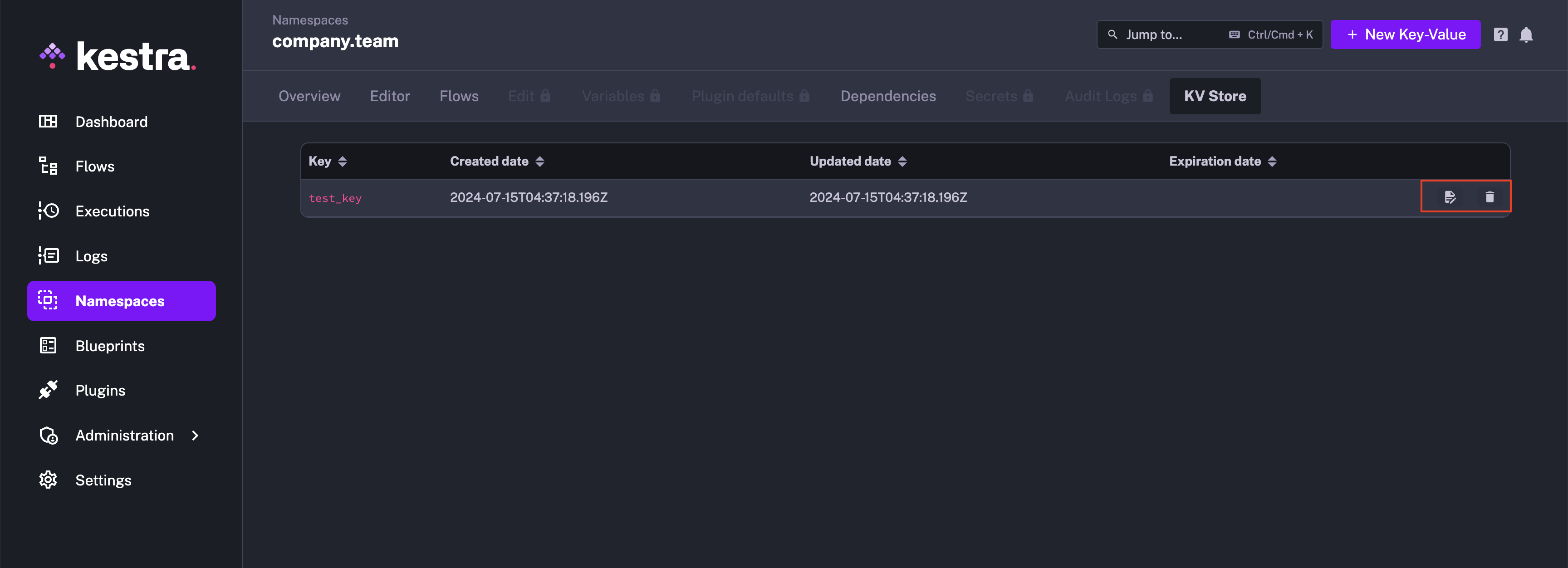
Update and Delete KV pairs from the UI
You can edit or delete any KV pair by clicking on the Edit button on the right side of each KV pair.
CODE: How to Create, Read, Update and Delete KV pairs in your flow code
Create a new KV pair with the Set task in a flow
To create a KV pair from a flow, you can use the io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Set task. Here's an example of how to create a KV pair in a flow:
id: add_kv_pair
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: download
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.http.Download
uri: https://huggingface.co/datasets/kestra/datasets/raw/main/csv/orders.csv
- id: set_kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Set
key: my_key
value: "{{ outputs.download.uri }}"
namespace: company.team # the current namespace of the flow is used by default
overwrite: true # whether to overwrite or fail if a value for that key already exists; default true
ttl: P30D # optional Time to Live (TTL) for the KV pair
- id: set_simple_kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Set
key: simple_string
value: hello from Kestra
- id: set_json_kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Set
key: json_kv
value: |
{
"author": "Rick Astley",
"song": "Never Gonna Give You Up"
}
- id: get_kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.output.OutputValues
values:
my_key: "{{ kv('my_key') }}"
simple_string: "{{ kv('simple_string') }}"
favorite_song: "{{ json(kv('json_kv')).song }}"
You can use the io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Set task to create or modify any KV pair. When modifying existing values, you can leverage the overwrite boolean parameter to control whether to overwrite the existing value or fail if a value for that key already exists. By default, the overwrite parameter is set to true so that the existing value is always updated.
Read KV pairs with Pebble
The easiest way to retrieve a value by key is to use the {{ kv('YOUR_KEY'') }} Pebble function.
Here is the full syntax of that function:
{{ kv(key='your_key_name', namespace='your_namespace_name', errorOnMissing=false) }}
Assuming that you retrieve the key in a flow in the same namespace as the one for which the key was created, you can simply use "{{ kv('my_key') }}" to retrieve the value:
id: read_kv_pair
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: log_key
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message: "{{ kv('my_key') }}"
When retrieving the key from another namespace, you can use the following syntax:
id: read_kv_pair_from_another_namespace
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: log_key_from_another_namespace
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message: "{{ kv('my_key', 'kestra.engineering.myproject') }}"
By default, when you try to retrieve a key that doesn't exist, the task using the "{{ kv('non_existing_key') }}" expression will run without errors — that expression will simply return null. If you prefer to instead throw an error when the key doesn't exist, you can set the errorOnMissing parameter to true:
id: read_non_existing_kv_pair
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: log_key_from_another_namespace
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.debug.Return
format: "{{ kv('non_existing_key', errorOnMissing=true) }}"
The function arguments such as the errorOnMissing keyword can be skipped for brevity as long as you fill in all positional arguments i.e. {{ kv(key='your_key_name', namespace='your_namespace_name', errorOnMissing=false) }} — the version below will have the same effect:
id: read_non_existing_kv_pair
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: log_key_from_another_namespace
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.debug.Return
format: "{{ kv('my_key', 'kestra.engineering.myproject', true) }}"
Read KV pairs with the Get task
You can also retrieve the value of any KV pair using the Get task. The Get task will produce the value output, which you can use in subsequent tasks. This option is a little more verbose but it has two benefits:
- More declarative syntax.
- Useful when you need to pass the current state of that value to multiple downstream tasks.
id: get_kv_pair
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: get
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Get
key: my_key
namespace: company.team
errorOnMissing: false
- id: log_key_get
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message: "{{ outputs.get.value }}"
Read and parse JSON-type values from KV pairs
To parse JSON values in Kestra's templated expressions, make sure to wrap the kv() call in the json() function, e.g. "{{ json(kv('your_json_key')).json_property }}".
The following example demonstrates how to parse values from JSON-type KV pairs in a flow:
id: kv_json_flow
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: set_json_kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Set
key: favorite_song
value: |
{
"author": "Rick Astley",
"song": "Never Gonna Give You Up",
"album": {
"name": "Whenever You Need Somebody",
"release_date": "1987-11-16"
}
}
- id: parse_json_kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message:
- "Author: {{ json(kv('favorite_song')).author }}"
- "Song: {{ json(kv('favorite_song')).song }}"
- "Album name: {{ json(kv('favorite_song')).album.name }}"
- "Album release date: {{ json(kv('favorite_song')).album.release_date }}"
- id: get
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Get
key: favorite_song
- id: parse_json_from_kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message: "Country: {{ json(outputs.get.value).album.name }}"
Read keys by prefix with the GetKeys task
If you want to check if some values already exist for a given key, you can search keys by prefix:
id: get_keys_by_prefix
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: get
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.GetKeys
prefix: "test_"
namespace: company.team
- id: log_key_prefix
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message: "{{ outputs.get.keys }}"
The output will be a list of keys - if no keys were found, an empty list will be returned.
Delete a KV pair with the Delete task
The io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Delete task will produce the boolean output deleted to confirm whether a given KV pair was deleted or not.
id: delete_kv_pair
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: kv
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.kv.Delete
key: my_key
namespace: company.team
errorOnMissing: false
- id: check_if_deleted
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message: "{{ outputs.kv.deleted }}"
API: How to Create, Read, Update and Delete KV pairs via REST API
Let's look at how you can interact with the KV Store via the REST API.
Create a KV pair
The API call to set the KV pair follows the structure:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/kv/{key} -d '<value>'
For example:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/company.team/kv/my_key -d '"Hello World"'
The above curl command will create the KV pair with key my_key and the Hello World string value in the company.team namespace. The API does not return any response.
Read the value by key
You can get any particular KV pair using:
curl -X GET -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/kv/{key}
For example:
curl -X GET -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/company.team/kv/my_key
This will retrieve a KV pair with the key my_key in the company.team namespace. The output of the API will contain the data type of the value and the retrieved value of the KV pair:
{"type": "STRING", "value": "Hello World"}
Read all keys in the namespace
You can list all keys in the namespace as follows:
curl -X GET -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/kv
The curl command below will return all keys in the company.team namespace:
curl -X GET -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/company.team/kv
The output will be returned as a JSON array of all keys in the namespace:
[
{"key":"my_key","creationDate":"2024-07-27T06:10:33.422Z","updateDate":"2024-07-27T06:11:08.911Z"},
{"key":"test_key","creationDate":"2024-07-27T04:37:18.196Z","updateDate":"2024-07-27T04:37:18.196Z"}
]
Delete a KV pair
You can delete any KV pair using the following API call:
curl -X DELETE -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/kv/{key}
This call returns a boolean indicating whether the key was deleted.
For example, the following curl command will return false because the key non_existing_key does not exist:
curl -X DELETE -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/company.team/kv/non_existing_key
However, when we try to delete a key my_key which exists in the company.team namespace, the same API call will return true:
curl -X DELETE -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8080/api/v1/namespaces/company.team/kv/my_key
TERRAFORM: How to Create, Read, Update and Delete KV pairs via Terraform
Create a KV pair
You can create a KV pair via Terraform by using the kestra_kv resource.
Here is an example of how to create a KV pair:
resource "kestra_kv" "my_key" {
namespace = "company.team"
key = "my_key"
value = "Hello Woprld"
type = "STRING"
}
Read a KV pair
You can read a KV pair via Terraform by using the kestra_kv data source.
Here is an example of how to read a KV pair:
data "kestra_kv" "new" {
namespace = "company.team"
key = "my_key"
}
As with anything in Terraform, you can manage the state of your KV resources by adjusting the Terraform code and running the terraform apply command to create, update, or delete your KV pairs.
Was this page helpful?